Website Migration SEO Breakdown: How To Fix It, Avoid It & Impact?
Website Migration SEO: What’s Wrong?
Drop in Clicks and Impressions due to a Poor CMS migration at an enterprise level.
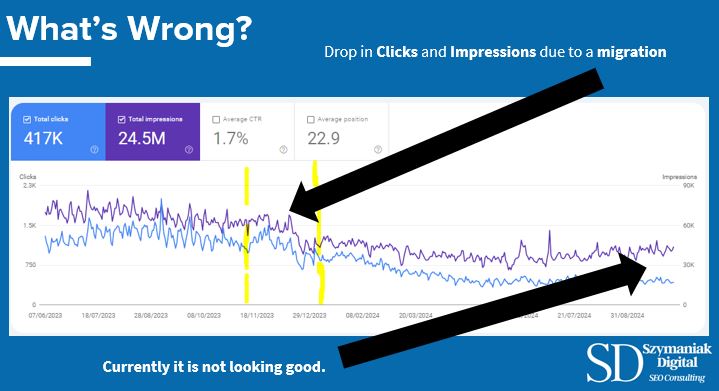
A Shopify website has undergone a migration without much thought about the technical aspects of SEO. The main causes of this large amount of loss in clicks and impressions have been caused by:
Duplicate Content: Crawling & Indexing – The site is being overrun with unnecessary URLs being crawled.
No actual backup of the site and its database.
When speaking to the Digital Marketing Director & Manager, the Staging site to test the whole migration (test redirects, duplicate content, canonicals, internal links, etc.) was made live too soon, meaning that the Google Bot started crawling the site before it was fully migrated.
Redirect mapping (list of URLs you want to appear on your site, so mapping out the current URLs to the new ones) has seen a limited scope because the site hasn’t been crawled by both Screaming Frog or any similar crawler like Botify, and the historical URL data in Google Search Console (GSC) using search analytics for sheets haven’t been accessed. This means that Google Bot could only identify and crawl a limited number of the URLs that had authority, as these should have been redirected and only about 35% of URLs have been mapped out.
Some of the most important aspects that should have been checked before migration are the Robots.txt, Sitemaps, Internal links, Hreflang (in this case no as this wasn’t an international migration), Structured data, URL structure, Mobile setup, and Pagination. Without this Konrad Szymaniak (Enterprise SEO Consultant), knows there is still a lot of work to do to fix the identified errors after deep analysis of the hierarchy of the site, keyword and visibility index drops (identified in Sistrix), and URL authority (backlink profile) which was lost due to a poor SEO-minded migration.
The website migration wasn’t domain-related therefore a new Google Search Console account does not need to be created, as the migration was CMS-based.
Poor Website SEO Migration: How To Fix It & Avoid It?
How To Fix Poor Website Migration SEO: Case Study of Shopify Site in the Outdoor Sector
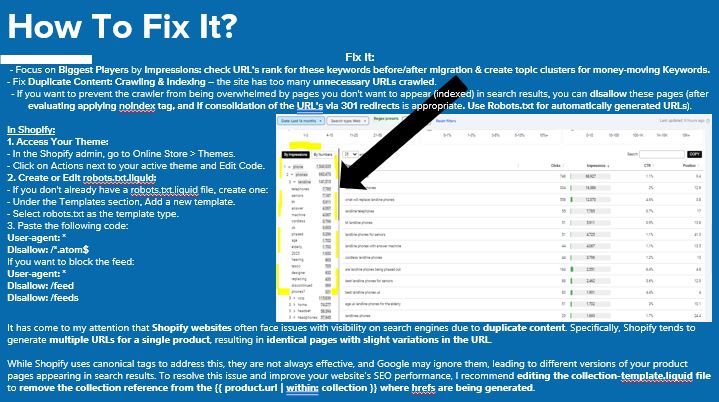
To fix SEO issues on Shopify websites, it’s important to focus on the most impactful elements. Start by identifying the top-performing keywords and tracking the rankings of these URLs before and after migration. For money-driving keywords, organise them into topic clusters to maximise visibility.
Duplicate Content Fix After a Poor Site Migration
Duplicate content is another major concern, as unnecessary URLs can make the crawler tired, wasting that important crawl budget. To avoid overwhelming the search engine, disallow non-essential URLs using the robots.txt file and consider applying noindex tags or consolidating URLs through 301 redirects.
Shopify often generates duplicate URLs for the same product, which can confuse search engines and hurt visibility. Although Shopify uses canonical tags to solve this, they’re not always reliable, and Google might overlook them. To further resolve this, edit the collection-template.liquid file to remove the collection reference from the URL structure, which helps avoid different versions of the same page being indexed.
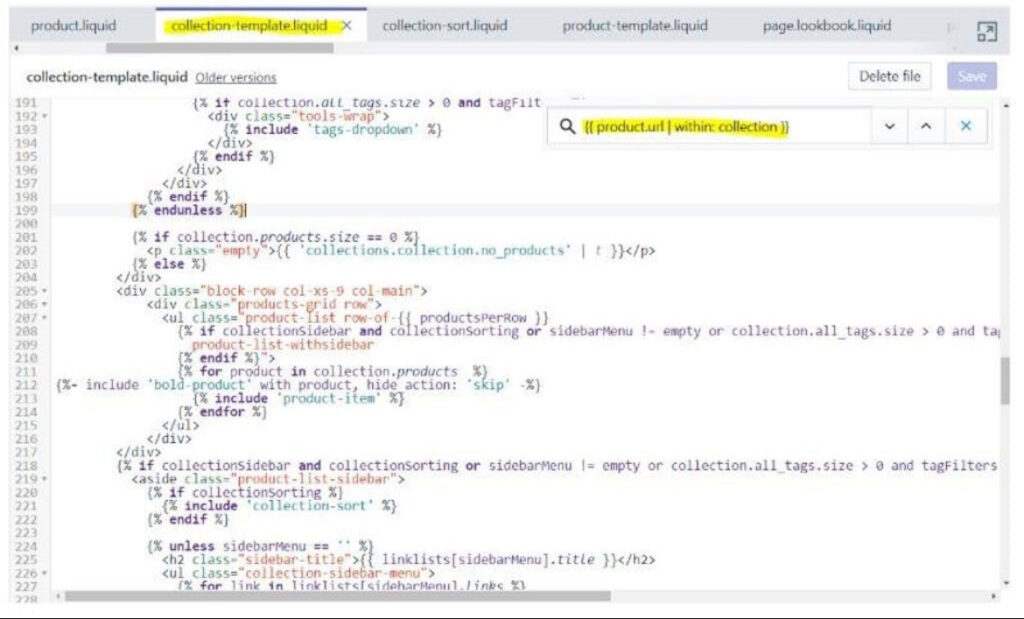
Key Fixes:
- Track URL rankings and traffic for high-impression keywords before and after migration.
- Build topic clusters for money-driving keywords. Use Google Search Console and Google Analytics (GA4).
- Prevent duplicate content by disallowing irrelevant URLs with robots.txt or using noindex tags.
- Modify the collection-template.liquid file to prevent multiple URL variations for the same product.
Step-by-Step Recommendations In Shopify (new site):
- Access Your Theme:
- In the Shopify admin, go to Online Store > Themes.
- Click on Actions next to your active theme and Edit Code.
- Create or Edit robots.txt.liquid:
- If you don’t already have a robots.txt.liquid file, create one:
- Under the Templates section, Add a new template.
- Select robots.txt as the template type.
- Paste the following code:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /*.atom$ - If you want to block the feed:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /feed
Disallow: /feeds
How To Avoid Poor Website SEO Migration: Case Study of Shopify Site in the Outdoor Sector
Before starting any site migration, it’s crucial to take several steps to avoid major issues. First, always create a full backup of your site and database so that you can restore everything if needed. Test the migration on a staging site, checking redirects, duplicate content, canonicals, and internal links. After setting up your hosting environment, ensure all files are transferred, and update DNS information and mail settings accordingly.
Redirect Mapping
Proper planning is essential, so create a redirect mapping list to ensure all URLs transition smoothly to the new structure. Review crawlability, custom URLs, alt text, canonical tags, robots.txt, sitemaps, internal links, and other SEO elements both before and after the migration. It’s important to audit the site, focusing on internal linking, server responses, and indexation, and recrawl to check for errors such as 404s and misapplied redirects.
If you’re enjoying this article, why not explore the Bournemouth SEO consultant services offered by Konrad Szymaniak, especially if you’re based in Bournemouth?
Key Steps:
- Backup your old site and database.
- Test the migration on a staging site for redirects, canonicals, and internal links.
- Set up hosting, transfer files, and update DNS and mail parameters.
- Create redirect mapping to ensure smooth URL transitions.
- Audit SEO elements (crawlability, canonical tags, internal links) before and after migration.
- Recrawl the site and check for errors such as 404s and 301s.
Website Migration SEO: Impact of the Fix & What to Expect?
Poor Website Migration: Impact of the Fix & What to Expect?
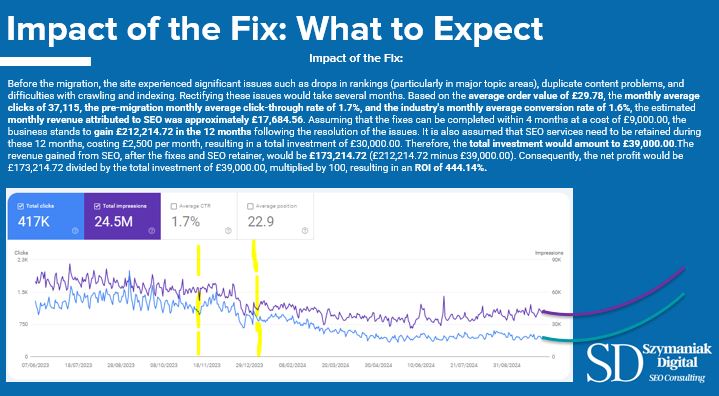
Before the site migration, the website faced several critical SEO challenges, including significant traffic drops, particularly in key topic areas, duplicate content, and issues with crawling and indexing. These problems were directly impacting the site’s performance and revenue, and it was estimated that resolving them would take approximately four months. To understand the financial implications, Konrad Szymaniak calculated the pre-migration revenue generated through SEO and projected the potential returns once these issues were fixed.
For further clarification, these projections are forecasts for the future, assuming that the Google algorithm is favouring the site. This means that the actual ROI may vary as Google changes its algorithm day by day.
At the time, the site had an average order value (AOV) of £29.78 and received 37,115 clicks per month. The click-through rate (CTR) was 1.7%, and the industry’s average conversion rate was 1.6%. Based on these numbers, the estimated monthly revenue from SEO was £17,684.56. If the SEO issues are fixed within four months, costing £9,000, the business could expect to generate approximately £212,214.72 in SEO revenue over the next 12 months.
Additionally, an SEO retainer of £2,500 per month would be necessary for ongoing optimisation, bringing the total investment to £39,000 over the year. After deducting this investment from the projected revenue, the business would gain £173,214.72, resulting in an ROI of 444.14%.
Detailed Breakdown
1. Pre-migration SEO Performance:
Before the migration, the site’s SEO issues were negatively affecting visibility and revenue. Here’s a summary of the key metrics:
- Average Order Value (AOV): £29.78
- Monthly Clicks: 37,115
- Click-through Rate (CTR): 1.7%
- Conversion Rate: 1.6% (industry average)
Using these figures, the estimated monthly SEO revenue was calculated as follows:
- Revenue = AOV (£29.78) × Clicks (37,115) × CTR (1.7%) × Conversion Rate (1.6%)
- Estimated Monthly SEO Revenue: £17,684.56
2. Cost of Fixing SEO Issues:
Fixing the SEO issues, including resolving duplicate content and improving crawling and indexing, was estimated to take four months at a cost of £9,000. Additionally, an SEO retainer of £2,500 per month for 12 months would be required to ensure ongoing success. This brings the total investment for the year to £39,000.
3. Revenue Projections After Fixes:
Once the SEO issues are resolved, it is expected that the website will regain its optimal performance (better performance than the pre-migration stage). Over the next 12 months, the projected SEO-driven revenue is:
- 12-month Revenue = £17,684.56 × 12 months = £212,214.72
4. Return on Investment (ROI):
After subtracting the total investment of £39,000 from the projected revenue of £212,214.72, the net profit would be:
- Net Profit = £212,214.72 – £39,000 = £173,214.72
Finally, calculating the ROI:
- ROI = (Net Profit ÷ Total Investment) × 100
- ROI = (£173,214.72 ÷ £39,000) × 100 = 444.14%
This substantial ROI of 444.14% highlights the significant financial benefit of resolving the SEO issues and maintaining ongoing optimisation efforts. By investing in these fixes, the business can significantly improve its revenue potential and achieve long-term growth.
Website SEO Migration: Conclusion
The migration resulted in a significant drop in clicks and impressions due to various SEO-related issues.
The primary causes of the decline were duplicate content, crawling and indexing problems, and internal linking issues.
To address these issues, focus on optimising high-performing keywords, resolving duplicate content, and improving website crawlability using techniques like robots.txt and canonical tags.
Before future migrations, implement a thorough testing process on a staging site to identify and rectify potential issues.
By addressing these SEO concerns, the business can potentially recover lost revenue and achieve a significant return on investment.
If you made it this far, and are interested in chatting away with Konrad Szymaniak (Independent Enterprise SEO Consultant) about all things migrations reach out to him via the contact page.
FAQs
Does website migration affect SEO?
Yes, changing a URL can affect your SEO by breaking internal links, creating 404 errors, losing backlinks, and causing delays in Google’s re-crawling process. To avoid these issues, set up a 301 redirect by adding the old and new URLs and selecting “301 Moved Permanently.” It’s best to avoid changing URLs unless necessary. The primary aspect is the money involved at the enterprise-level where many SEO professionals struggle to apply best practices.
How to migrate a website SEO?
Firstly, backup your site and database. Secondly, test the migration on a staging site for redirects, canonicals, and internal links. Thirdly, set up hosting, transfer files, and update DNS and mail parameters, then create redirect mapping to ensure smooth URL transitions. After you might want to audit SEO elements (crawlability, canonical tags, internal links) before and after migration. Lastly, recrawl the site and check for errors such as 404s and 301s.
Will domain migrations increase SEO traffic?
Yes, a well-managed domain migration can increase SEO traffic and improve a website’s visibility and search engine rankings. However, a poorly managed migration can lead to a loss of traffic and visibility. Here are some tips for a successful domain migration:
1. Have a plan: A solid plan can help ensure a smooth transition and minimize SEO pitfalls.
2. Use 301 redirects: 301 redirects signal to search engines that content has permanently moved from the old domain to the new one. This helps maintain search engine rankings.
3. Monitor ranking keywords: Track how many of the top ranking keywords from the original site shift to the new site.
Consider the changes.
The amount a website’s SEO is affected depends on the changes made and how effectively old pages are redirected. For example, redirecting everything to the homepage can lead to traffic loss. SEO value can take a long time to build and can be lost quickly during a migration. However, it’s possible to recover lost traffic if you move quickly enough

